
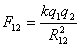
where R12 is the distance between the charges. k is a constant of proportionality known as the Coulomb constant, having the value 9 x 109 N.m2 / C2 in a vacuum.
![]() Note that the Coulomb constant, k, is
often replaced with (1/4π ε0), where
ε0is the permittivity of the vacuum (more later).
Note that the Coulomb constant, k, is
often replaced with (1/4π ε0), where
ε0is the permittivity of the vacuum (more later).
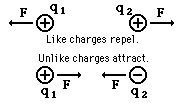
This is an extremely large force (sufficient to move Mt. Everest with an acceleration of 1cm/s2). The Coulomb is a very large unit. Typical macroscopic charges are measured in micro-coulombs (10-6 C).
 Notice
the
similarity
of
Coulomb's Law to Newton's Law of Gravitation
Notice
the
similarity
of
Coulomb's Law to Newton's Law of Gravitation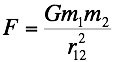
![]()
Dr. C. L. Davis
Physics Department
University of Louisville
email: c.l.davis@louisville.edu
