

where VAB = VB - VA is the potential difference between A and B.
1 Volt = 1 Joule/Coulomb (J/C)
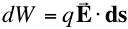

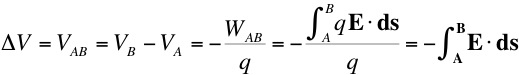

 The
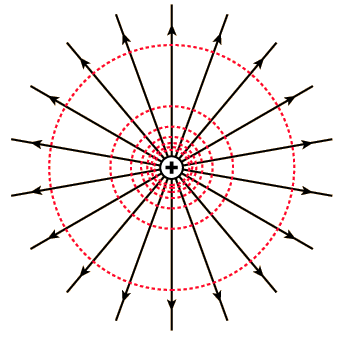
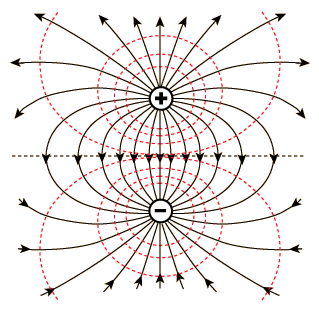
electric field is a conservative field.
The
electric field is a conservative field.

 Food
for thought....
Food
for thought.... Exactly equivalent to gravity, it
is CHANGES
in potential difference,
Exactly equivalent to gravity, it
is CHANGES
in potential difference, 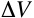 ,
which are defined. To obtain absolute values
of V physicists usually define V = 0 at
infinity. But this is an arbitary definition;
in engineering applications it is often convenient
to define the earth as V = 0.
,
which are defined. To obtain absolute values
of V physicists usually define V = 0 at
infinity. But this is an arbitary definition;
in engineering applications it is often convenient
to define the earth as V = 0.
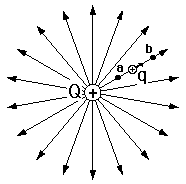


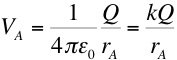
For continuous distributions of charge we may write,
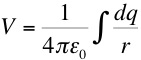
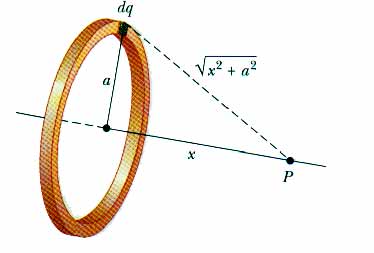
The electric potential due to a
continuous charge distribution can
be calculated in a similar manner to
the electric field due to such a
distribution. For example the
potential at point P due to a
uniform ring of charge (below).

![]()
In the period that Einstein was active as
a professor, one of his students came to him and said: "The
questions of this year's exam are the same as last years!"
"True," Einstein said, "but this year all answers are
different."
Albert Einstein
Dr. C. L. Davis
Physics Department
University of Louisville
email: c.l.davis@louisville.edu
